Blog
Top Tips for Choosing the Right Flexible PCB Material for Your Projects
In the rapidly evolving electronics industry, the demand for flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) has surged significantly, driven by the increasing miniaturization of components and the need for lightweight, space-saving designs. The global flexible PCB market is projected to reach approximately $40 billion by 2024, according to a report by Market Research Future, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10%. This growth highlights the importance of selecting the appropriate flexible PCB material, as the material choice influences factors such as the performance, cost, and durability of the final product.
When embarking on projects that require flexible PCBs, understanding the various types of flexible PCB materials available is crucial. Options range from Polyimide (PI) and Polyester (PET) to more advanced materials designed for specific applications. Each material exhibits unique characteristics, including thermal stability, chemical resistance, and electrical performance, which can dramatically impact the overall effectiveness of the PCB. According to IPC (Institute of Printed Circuits), the right selection of flexible PCB material can lead to significant enhancements in reliability and functionality, making it a critical consideration for engineers and designers alike.
In conclusion, the process of choosing flexible PCB materials should be underpinned by rigorous analysis and an understanding of the project requirements. The right flexible PCB material not only ensures optimal performance but also aligns with industry trends and innovations, paving the way for successful electronic designs in a competitive marketplace.

Key Considerations for Selecting Flexible PCB Materials in Design
When selecting the right flexible PCB material for your design projects, there are several key considerations that engineers should keep in mind. One fundamental aspect is the application environment; materials must withstand factors like temperature fluctuations, humidity, and mechanical stress. According to industry reports, such as those from IPC and other circuit board manufacturing associations, about 40% of flexible PCB failures can be attributed to material inadequacies under environmental stress. Therefore, choosing materials with appropriate thermal and mechanical properties is critical to ensuring reliability and longevity.
Another important consideration is the electrical performance of the flexible PCB material. The dielectric constant and loss tangent of the material influence signal integrity and can lead to performance issues in high-frequency applications. Data from market studies indicate that materials with lower loss tangents are increasingly sought after, especially in the automotive and telecommunications sectors, which are projected to grow by 7.5% annually. As the demand for high-speed data transfer and miniaturization of devices increases, utilizing materials that meet these stringent criteria becomes essential. Balancing performance requirements with manufacturing capabilities can significantly affect the overall success of a project.
Understanding the Role of Dielectric Constants in Flexible PCBs
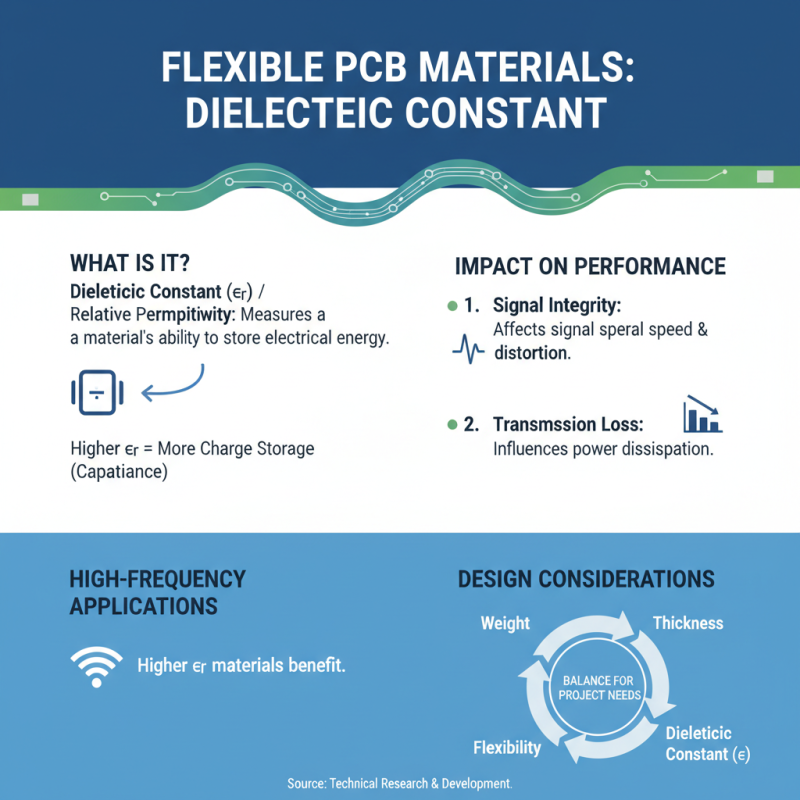
When selecting the right flexible PCB material for your projects, understanding the dielectric constant is crucial. The dielectric constant, or relative permittivity, indicates how well a material can store electrical energy in an electric field. This property significantly influences the performance of flexible PCBs, particularly concerning signal integrity and transmission loss. A higher dielectric constant typically means better capacitance, which can be beneficial for high-frequency applications. However, it's essential to balance this with the material's weight, thickness, and flexibility to meet project requirements.
Consider the specific needs of your project when choosing materials. For applications where high frequency and minimal signal loss are critical, opt for materials with a stable dielectric constant across varying environmental conditions. Another tip is to evaluate the thermal characteristics, as the dielectric constant can change with temperature fluctuations. Additionally, consider the manufacturing processes involved, as some materials may require specialized equipment or techniques to ensure optimal performance. By carefully weighing these factors, you can select a flexible PCB material that meets your design goals and enhances overall performance.
Evaluating Temperature Tolerance in Flexible PCB Materials
When selecting flexible PCB materials for your projects, evaluating temperature tolerance is paramount. Flexible PCBs are exposed to a variety of environmental conditions during their operational lifecycle, which can significantly impact their performance and durability. According to a report by IPC, the largest association for the electronics industry, a substantial percentage of PCB failures are attributed to thermal stress. Hence, understanding the temperature ranges that materials can withstand without losing functionality is crucial for project success.
Typically, flexible PCB materials have specified temperature ratings that determine their maximum operational temperature. For example, polyimide films, commonly used in high-performance applications, can tolerate temperatures up to 250°C (482°F) for short durations. In contrast, other materials might only support maximum temperatures in the range of 130°C (266°F). Thermal cycling can also lead to material fatigue, which emphasizes the need for selecting materials that not only boast high thermal limits but also display stable performance with repeated temperature fluctuations. A study cited by the Journal of Electronics Manufacturing shows that flexible PCBs subjected to harsh temperature variations can see decreased reliability by up to 30%, underscoring the importance of rigorous temperature evaluation during the material selection process.
Consideration of temperature tolerance extends beyond peak ratings; it involves assessing the material's thermal conductivity, coefficient of thermal expansion, and long-term stability under elevated temperatures. Choosing the right flexible PCB material with optimal temperature tolerance can lead to enhanced performance, longevity, and ultimately, a reduction in failures, making it a vital factor for engineers and designers in the electronics sector.
Top Tips for Choosing the Right Flexible PCB Material for Your Projects - Evaluating Temperature Tolerance in Flexible PCB Materials
| Material Type | Max Operating Temperature (°C) | Thermal Expansion Coefficient (ppm/°C) | Dielectric Constant | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyimide | 200 | 30 | 3.5 | Aerospace, automotive |
| PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) | 150 | 60 | 2.9 | Consumer electronics |
| FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) | 200 | 20 | 2.1 | High-frequency applications |
| PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | 260 | 100 | 2.0 | Space applications, RF circuits |
| LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer) | 230 | 50 | 3.0 | Telecommunications, high-speed data |
Impact of Mechanical Properties on Flexible PCB Performance
When selecting materials for flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs), understanding the influence of mechanical properties is crucial to ensuring optimal performance. A recent industry report indicates that mechanical attributes such as tensile strength, elongation at break, and bending fatigue significantly impact the durability and longevity of flexible PCBs. For example, materials with high elongation, typically over 100%, can endure more significant bending and flexing without losing electrical conductivity. This is particularly vital in applications requiring repeated motion, such as wearables and consumer electronics.
Moreover, the performance of flexible PCBs under mechanical stress is closely related to their thermal properties and adhesive characteristics. A study published by the IPC (Institute for Printed Circuits) highlights that flexible PCBs composed of materials with low thermal expansion coefficients exhibit better dimensional stability under temperature fluctuations. This stability is essential for maintaining the integrity of connections and preventing failure in high-performance applications. Materials with robust adhesive properties also ensure better bonding during flex conditions, thereby elevating their mechanical reliability. Ultimately, selecting the right material based on these mechanical properties will lead to more resilient and efficient flexible PCB designs.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Different Flexible PCB Material Options
When selecting the right flexible PCB material for your project, conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis is crucial to make an informed decision. Different materials, such as polyimide, polyester, and thermoplastics, offer varying properties and price points, influencing overall project costs. While polyimide materials provide exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, their price is typically higher than alternatives. Understanding the specific requirements of your application will allow you to weigh these attributes against potential costs effectively.
Additionally, considering the production volume and application environment is essential in your cost-benefit analysis. For instance, if your project involves high-speed electronics, investing in high-quality materials may reduce long-term failure rates and maintenance costs. Conversely, for less demanding applications, lower-cost materials might suffice, enabling budget savings without significantly compromising performance. Ultimately, the right choice balances material properties, manufacturing processes, and financial constraints to deliver the best value for your project.
Related Posts
-

Understanding Rigid Flex PCBs: A Comprehensive Guide to This Hybrid Technology
-

Future Trends of Flex Circuit Board at 2025 China Import and Export Fair Insights and Data
-
Top 5 Benefits of Using Flexible Printed Circuits in Modern Electronics
-

How to Master Circuit Board Design: Essential Tips for Beginners
-

Embracing Innovation: The Future of PCB Printed Circuit Board Technology and Applications
-
Solutions for Sourcing the Best PCB Circuit Boards Globally: Your Comprehensive Guide
